The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck. Despite its size, it may play a critical role in regulating many processes in the body. Through hormone secretion, it may influence metabolism, growth, energy balance, and overall health. This article highlights the major functions of the thyroid and its importance for well-being.
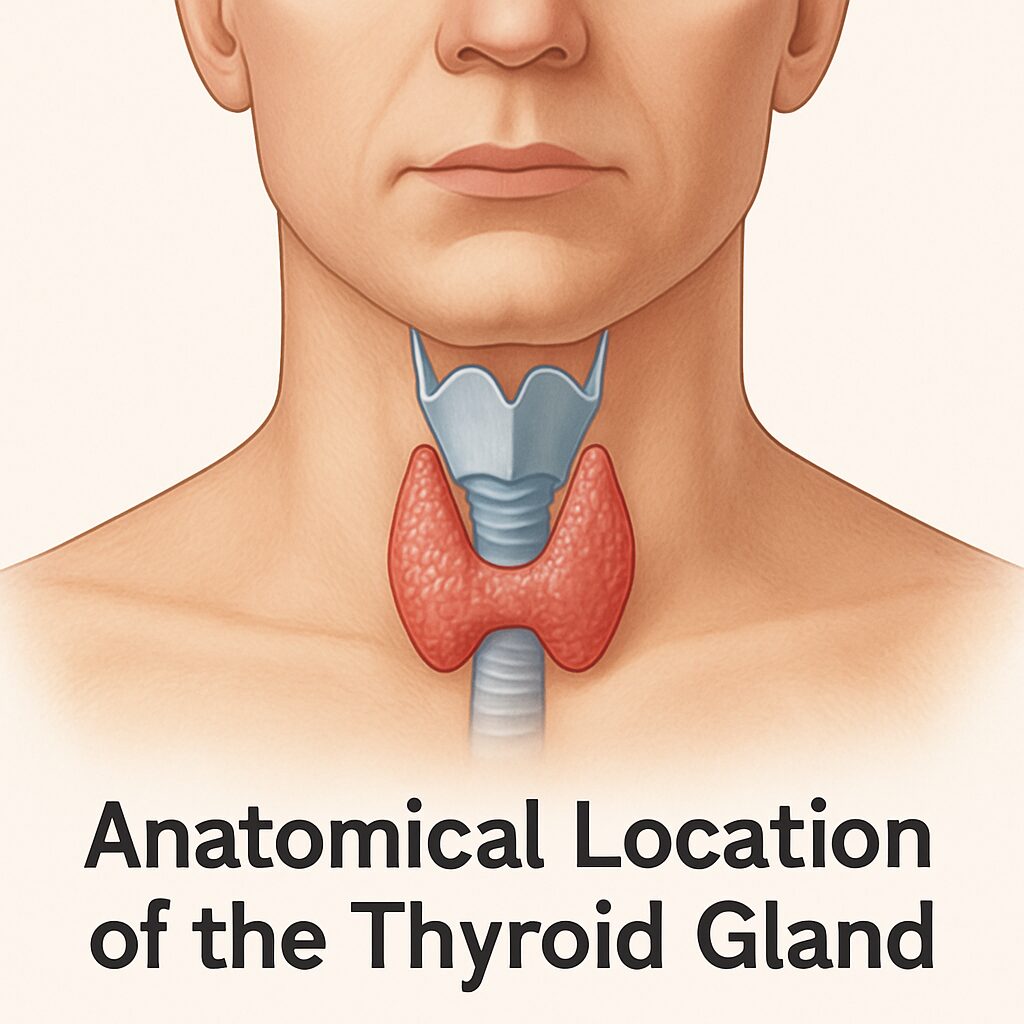
1. Location and Structure
The thyroid sits in front of the trachea and is divided into right and left lobes connected by an isthmus. Although small, it has a rich blood supply and may be evaluated through medical imaging or physical examination when needed.
2. Thyroid Hormones
The main hormones produced are thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). T3 is the more active form, and both may regulate metabolism and energy use. The thyroid also secretes calcitonin, which may contribute to calcium regulation in the body.
3. Regulation of Metabolism
Thyroid hormones may influence the basal metabolic rate, meaning how much energy the body consumes at rest. Proper hormone balance often supports energy use, body temperature regulation, and vitality. Insufficient levels may lead to fatigue or weight gain, while excess may cause restlessness or weight loss.
4. Growth and Development
In children and adolescents, thyroid hormones are essential for bone growth and brain development. Deficiency during growth years may affect learning ability and physical development, which is why monitoring thyroid health in this period is important.
5. Cardiovascular and Temperature Control
Thyroid hormones may affect heart rate and circulation. Balanced hormone secretion supports steady heartbeat and proper blood flow. They also help regulate body temperature, meaning imbalances may cause unusual sensitivity to cold or heat.
6. Nervous System and Emotions
Hormones from the thyroid may influence brain activity and emotional balance. Low function is sometimes linked to fatigue or depression, while overactivity may result in anxiety, nervousness, or difficulty sleeping.
7. Digestion and Weight Balance
Metabolic activity affects how quickly food is processed. Overactive thyroid function may lead to weight loss, while reduced function may lead to gradual weight gain. Since many factors contribute to weight changes, thyroid function is usually considered along with other health aspects.
8. Links with Immunity
Some thyroid conditions, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, are autoimmune in nature. This means the immune system mistakenly affects thyroid tissue. Such interactions may influence both gland activity and general health.
🍀
The thyroid is small but may play a vital role in metabolism, growth, cardiovascular health, and emotional balance. Ongoing fatigue, weight change, or mood swings may sometimes indicate thyroid issues. Regular check-ups and professional care may help maintain thyroid health and overall well-being.
References and Further Reading
National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Thyroid Function and Health
World Health Organization (WHO) – Endocrine Health Overview
American Thyroid Association (ATA) – Patient Resources
※ This article is for general informational purposes only. Health conditions may vary individually, and professional medical advice is generally recommended if symptoms persist.